Hardwood species of maple are found throughout northern France. There is a total planted area estimated at 59 000 ha. Maples are tall trees, up to 30m in height, with very cylindrical trunks and a medium growth rate allowing them to be harvested at around 80 years.
Wood description
Sawn timber shows whitewood, sometimes slightly yellowish. Sapwood is not distinctive.
Preserving
Maple can be easily treated. Once impregnated, it can be used as Class 4 timber (in contact with non-salty water).
Physical and mechanical properties
Sycamore maple is a moderately heavy and moderately hard wood. Expansion/contraction is minimal. It is resistant to wear and tear, is solid, elastic and flexible. It is highly susceptible to discolouration, and yellows markedly when exposed to air and light.
| Average density | 630 kg/mᶟ |
| Total average volumetric shrinkage | 12.3 % |
| Brinell hardness perpendicular to the fibres | 30 N/mm² |
| ]Modulus of rupture under bending | 110 MPa |
| Breaking stress under axial compression | 54 MPa |
| Modulus of longitudinal elasticity under bending | 10 500 MPa |
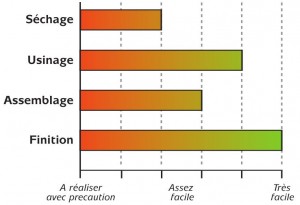
Conditions of implementation
Principales utilisations
Maple is mainly used for joinery, interior fittings, veneer, furniture, flooring, turned pieces and marquetry.


![2 R UMAX Vista-S6E V2.0 [4]�](http://frenchtimber.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/erable_sycomore-internet-180x180.jpg)