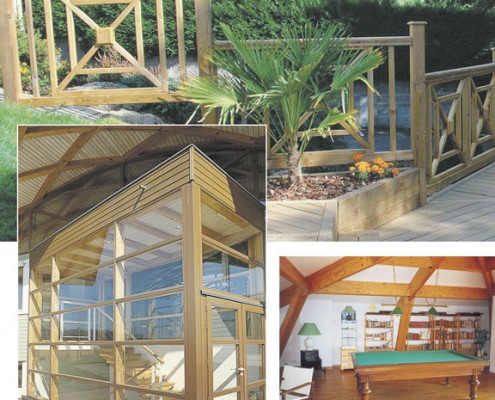
Widespread specie in France, it is present on all northern half of France, standing on 1 130 000 ha. Due to its good resistance to cold weather, Scots pine is often seen in the French mountainous areas. This specie, which growths slowly, features a tall and straight trunk.
Wood description
Scots pine shows a distinct yellowish white sapwood and a pinkish to reddish-brown heartwood. Generally straight-grained with fine texture.
Preserving
Scots pine’s heartwood is naturally resistant against mushrooms but is hardly impregnable. Sapwood is easily impregnable. Sawn timber is usable in both Class 4 and 5 after vacuum pressure treatment.
Physical and mechanical properties
The wood has good mechanical resistance. It ranges from light to moderately heavy. Very hard knots can sometimes weaken its adhesiveness. The wood is fissile and quite flexible; expansion/contraction is minimal.
| Average density | 550 kg/mᶟ |
| Total average volumetric shrinkage | 14.1 % |
| Brinell hardness perpendicular to the fibres | 18 N/mm² |
| Modulus of rupture under bending | 109 MPa |
| Breaking stress under axial compression | 56 MPa |
| Modulus of longitudinal elasticity under bending | 14 500 MPa |
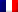
Conditions of implementation
Grading
Download
Softwood grading
Main uses
Scots pine is commonly used for interior (moulding, skirting boards, panelling and flooring …) and exterior joinery as well as frameworks. Scots pine is also appreciated for furniture and exterior fittings (acoustic screens, guard rail, cladding, decking and footbridge).