Maritime pines, standing on over 10% of the total French forest, cover about 1 360 000 ha. There are tall trees, with brownish-red cracked bark.
Wood description
Maritime pine shows a distinct yellowish white sapwood and a reddish heartwood. It is mainly straight-grained with medium texture.
Preserving
Sapwood is not naturally durable, though easily impregnable by treatment (either by impregnation or by vacuum pressure). Heartwood is naturally durable. After vacuum pressure treatment, it can be graded in both Classes 4 and 5.
Physical and mechanical properties
It is hard, heavy and resistant. Quite hard knots can sometimes weaken its adhesiveness. The wood is fissile and flexible; expansion/contraction is minimal. It has good compression resistance, but is less elastic during bending than Scots pine. The wood has a high resin content.
| Average density | 560 kg/mᶟ |
| Total average volumetric shrinkage | 11.9 % |
| Brinell hardness perpendicular to the fibres | 20 N/mm² |
| Modulus of rupture under bending | 90 MPa |
| Breaking stress under axial compression | 47 MPa |
| Modulus of longitudinal elasticity under bending | 10 200 MPa |
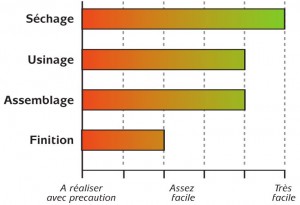
Conditions of implementation
Grading
Download
Softwood grading
Main uses
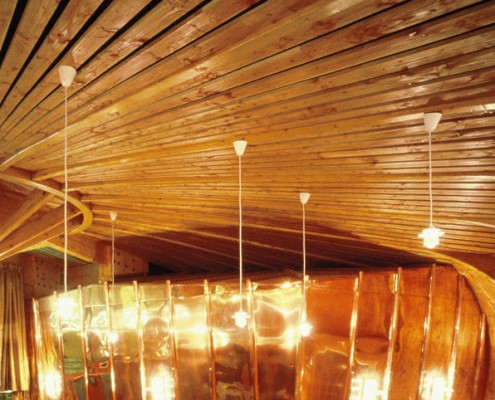
The main uses for maritime pine sawn timber are joinery, both interior (moulding, skirting boards, flooring and panelling) and exterior, as well as furniture and frameworks. It is also commonly used, when treated, for exterior fittings (cladding, exterior urban furniture). Finally, it is a widespread specie used for packaging, crates and pallets production.